Books cited in Ganga Library
Videos/Films
History of Discovery
Humor/Quotations
Statistical analysis of prize
Patents
Copyrights/Economics
Bearing Laureate's Name
US Government
Drug Discoveries
Immigration History
Educational
Languages
- Home
- About Us
- Alfred Nobel
- Nobel Laureates
- General Prize Info
- Nat'l Medal Laureates
- Volunteers
- Advertisers


Read Nobel Minds, Get Inspired!
Digital, Global, Multilingual, Interactive, Nonprofit
Robert J. Lefkowitz MD
Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2012
National Medal of Science- Biological Sciences 2007 USA
Physician- Cardiologist, Scientist. G-protein-coupled receptors;
approximately half of all medicines used today use this kind of receptor.
"Strong family history of coronary artery disease ... at age 50 I had quadruple bypass surgery [1994]. I minimize my risk factors with daily physical exercise, a vegetarian diet and appropriate medications".
Patents
| Publication: | 1/10 |
| Publication No: | US 10682397 B2 |
| Title: | Methods of treating fragile X syndrome and related disorders |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | June 16, 2020 |
| Filing Date: | Nov. 30, 2016 |
| Inventors: | Benjamin David Auerbach, Mark Firman Bear, Laura Jane Stoppel, Robert J. Lefkowitz |
| Assignee: | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology, Duke University |
| Abstract: | Disclosed herein are novel methodologies of treating fragile X syndrome and related disorders by inhibiting mGlu5-relevant signaling pathways via the reduction of β-arrestin2 protein levels or the diminution of mGlu5 and β-arrestin2 protein interactions. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 2/10 |
| Publication No: | US 7413876 B2 |
| Title: | Expression of G protein coupled receptors in yeast |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | Aug. 19, 2008 |
| Filing Date: | Nov. 23, 2004 |
| Inventors: | Klim King, Henrick G. Dohlman, Marc G. Caron, Robert J. Lefkowitz |
| Assignee: | Duke University Medical Center |
| Abstract: | Disclosed is a transformed yeast cell containing a first heterologous DNA sequence which codes for a mammalian G protein-coupled receptor and a second heterologous DNA sequence which codes for a mammalian G protein a subunit (mammalian Gα). The first and second heterologous DNA sequences are capable of expression in the cell, but the cell is incapable of expressing an endogenous G protein a-subunit (yeast Gα). The cells are useful for screening compounds which affect the rate of dissociation of Gα from Gβγ in a cell. Also disclosed is a novel DNA expression vector useful for making cells as described above. The vector contains a first segment comprising at least a fragment of the extreme amino-terminal coding sequence of a yeast G protein-coupled receptor. A second segment is positioned downstream from the first segment (and in correct reading frame therewith), with the second segment comprising a DNA sequence encoding a heterologous G protein-coupled receptor. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 3/10 |
| Publication No: | US 7615610 B2 |
| Title: | Methods of treating fragile X syndrome and related disorders |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | Nov. 10, 2009 |
| Filing Date: | Jan. 26, 2004 |
| Inventors: | Sudha Shenoy, Robert J. Lefkowitz |
| Assignee: | Duke University |
| Abstract: | The present invention relates to a modified arrestin which includes an arrestin molecule and a ubiquitin molecule. This modified arrestin has an increased affinity for a GPCR, and traffics with the GPCR into endosomes. The present invention further relates to a method of screening compounds and sample solutions for a GPCR agonist, antagonist, inverse agonist, or desensitization active compound. The modified arrestin is useful in the methods of the present invention. |
| Representative Figure: | |
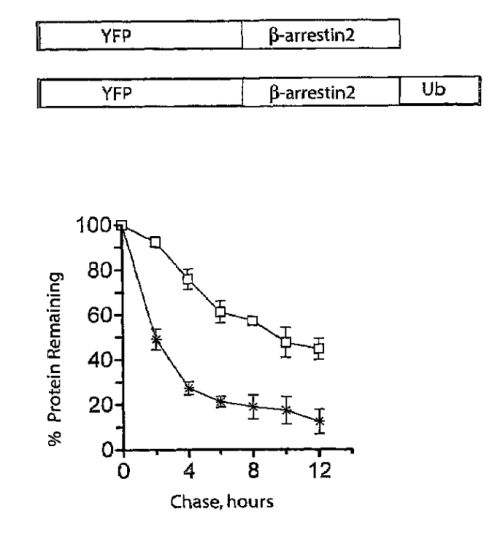 | |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 4/10 |
| Publication No: | AU 2003287006 B2 |
| Title: | Expression of G protein coupled receptors in yeast |
| Publication Type: | Australian Patent |
| Publication Date: | March 18, 2010 |
| Filing Date: | Oct 20, 2003 |
| Inventors: | Walter J. Koch, Robert J. Lefkowitz, Claude A. Piantadosi, Jonathan S. Stamler, Erin J. Whalen |
| Assignee: | Duke University |
| Abstract: | Desensitization of receptors that control disease is prevented by inhibiting G-protein receptor kinases. This has applicability, e.g., for patients with heart failure or on a left ventricular heart device or a heart pump after surgery or about to undergo surgery and at high risk for a cardiac event of on an opiate or addicted to opiate or with cystic fibrosis or rheumatoid arthritis. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 5/10 |
| Publication No: | US 7060871 B2 |
| Title: | Use of exogenous β-adrenergic receptor and β-adrenergic receptor kinase gene constructs to enhance myocardial function |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | June 13, 2006 |
| Filing Date: | June 28, 2002 |
| Inventors: | Walter J. Koch, Robert J. Lefkowitz, Carmelo A. Milano, Howard A. Rockman |
| Assignee: | Duke University |
| Abstract: | The present invention deals with gene therapy for treating chronic heart failure and other cardiac disease states which are accompanied by a reduced number or functioning of myocardial beta-adrenergic receptors (β-AR). β-AR receptor function is augmented in transgenic animals by delivery and expression of a beta-2-adrenergic receptor gene or a gene encoding a beta adrenergic receptor kinase inhibitor, resulting in increased in vivo left ventricular function. The present invention includes recombinant plasmid vectors, alternative beta-adrenergic receptor gene delivery strategies, and transgenic mice carrying a β-AR transgene, a β-ARK transgene, or a β-ARK inhibitor transgene. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 6/10 |
| Publication No: | US 6605424 B1 |
| Title: | Method of detecting inhibitors of agonist-specific desensitization |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | Aug. 12, 2003 |
| Filing Date: | May 1, 2000 |
| Inventors: | Robert J. Lefkowitz, Martin J. Lohse, Jeffrey L. Benovic, Marc G. Caron |
| Assignee: | Duke University |
| Abstract: | The present invention relates to a method of inhibiting desensitization of a cell to the effects of a compound. The method comprises contacting the cell with an agent capable of inhibiting phosphorylation, by a protein kinase, of a receptor for the compound present on the surface of the cell. The present invention also relates to a method of screening a compound for its ability to inhibit desensitization. The method comprises: i) contacting a receptor specific kinase-containing sample with the compound under conditions such that interaction between receptor specific kinase present in the sample and the compound can occur, and ii) determining the ability of the receptor specific kinase to phosphorylate the receptor for which it is specific. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 7/10 |
| Publication No: | US 6528271 B1 |
| Title: | Inhibition of βarrestin mediated effects prolongs and potentiates opioid receptor-mediated analgesia |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | March 4, 2003 |
| Filing Date: | Dec.22, 1999 |
| Inventors: | Laura M. Bohn, Fang-Tsyr Lin, Marc G. Caron, Robert J. Lefkowitz |
| Assignee: | Duke University |
| Abstract: | The present invention provides a βarrestin knockout mouse useful for screeening compounds for efficacy in controlling pain, methods of controlling pain in subjects by inhibiting binding of %beta;arrestin to phosphorylated μ opioid receptors, and methods of screening a compound for activity in potentiating μ opioid receptor agonist activity (e.g., morphine activity) by determining whether or not said compound inhibits βarrestin binding to a phosphorylated μ opioid receptor.. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 8/10 |
| Publication No: | US 6683057 B1 |
| Title: | Method of inhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferation |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | March 4, 2003 |
| Filing Date: | Dec. 22, 1999 |
| Inventors: | Walter J. Koch, Robert J. Lefkowitz, Per-Otto Hagen |
| Assignee: | Duke University |
| Abstract: | he present invention relates, in general, to vascular smooth muscle proliferation and, in particular, to a method of inhibiting arterial and venous smooth muscle proliferation resulting, for example, from arterial injury or vein grafting. The invention also relates to an expression construct encoding a Gβγ inhibitor suitable for use in such a method. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 9/10 |
| Publication No: | US 6610532 B2 |
| Title: | Intracellular inhibitors of Gq protein signaling |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | Aug. 26, 2003 |
| Filing Date: | July 24, 1998 |
| Inventors: | Walter J. Koch, Robert J. Lefkowitz, Shahab A. Akhter, Louis M. Luttrell, Howard Rockman |
| Assignee: | Duke University |
| Abstract: | The present invention relates, in general, to myocardial hypertrophy and, in particular, to agents that inhibit cardiac Gq-coupled receptor signaling and to methods of inhibiting myocardial hypertrophy using same. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
| Publication: | 10/10 |
| Publication No: | US 5573908 A |
| Title: | Adrenergic receptor as a proto-oncogene |
| Publication Type: | United States Utility Patent |
| Publication Date: | Nov. 12, 1996 |
| Filing Date: | Dec. 20, 1993 |
| Inventors: | Lee F. Allen, Robert J. Lefkowitz, Marc G. Caron, Susanna Cotecchia |
| Assignee: | Duke Univesity |
| Abstract: | A recombinant cell comprising a host cell containing a recombinant DNA sequence is disclosed. The recombinant DNA sequence comprises vector DNA and DNA which encodes a mammalian adrenergic receptor. The host cell is one capable of undergoing proliferation in response to activation of the adrenergic receptor. In one specific embodiment of the foregoing, the adrenergic receptor includes a mutation in the third cytoplasmic loop thereof which renders the adrenergic receptor constitutively active, and the host cell undergoes proliferation in response to the constitutively active adrenergic receptor. Also disclosed are in vitro assays employing the foregoing which are useful for screening test compounds for antitumor and antiatherogenic activity, along with a diagnostic assay for detecting the oncogenic activation of cells in a patient. The diagnostic assay comprises collecting sample cells which express adrenergic receptors from the patient, and then detecting the presence or absence of a mutation in the adrenergic receptor which renders the receptor constitutively active. The presence of such a mutation indicates the oncogenic activation of the cells. |
| Representative Figure: | No Figure |
| Family | |
| Details | Google Patents USPTO Patent Database |
Discover Your Abilities and Aspirations!
 $10 $25 $50 $100 Other
$10 $25 $50 $100 Other
Tax Exempt 501(c)3 Non-Profit Organization
Any Currency
“…the peace that is found in libraries and laboratories…” - Louis Pasteur
Copyright © 2023 Ganga Library Inc.  All Rights reserved.;

Photo: Bengt Nyman, Painting Tim Tompkins - PaintHistory.com
Name: Robert J. Lefkowitz
Birth: 15 April, 1943, New York, USA
Institution: Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC, USA
Award: "for studies of G-protein-coupled receptors"
Subject: Biochemistry
Portion of cash: 1/2
National Medal of Science- Biological Sciences 2007 USA
Nobel Lecture at Uppsala University
National Medal of Science- Biological Sciences 2007 USA
Nobel Lecture at Uppsala University
Info
Vita
Publications
History of Discovery
Books
External Videos/Films
Humor/Other
Nobel Prize General Info.
Patents
Videos





